The Great Taste Shift: How GLP-1 Drugs Are Redefining Food Pleasure
The culinary world is undergoing a fascinating transformation, driven by the introduction and growing popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists, a class of drugs originally designed to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. These medications, including well-known names like semaglutide and liraglutide, are now redefining how we experience food pleasure. As they work to regulate appetite and improve metabolic health, they also alter our taste preferences and food consumption patterns. This shift is not just a medical phenomenon; it’s reshaping cultural and social perceptions of eating, challenging traditional notions of indulgence and satisfaction. This article delves into the profound implications of this change, exploring how these drugs are influencing our relationship with food and what it means for the future of gastronomy.
The Science Behind GLP-1 and Appetite Regulation

GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, is a hormone that plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation. When GLP-1 receptor agonists are administered, they mimic the effects of this hormone, enhancing insulin secretion, slowing gastric emptying, and promoting a feeling of satiety. This biochemical interplay not only aids in weight management but also alters taste perception and food enjoyment. Research suggests that these drugs can diminish cravings for high-calorie, high-fat foods, leading to healthier eating patterns. Understanding the science behind GLP-1’s influence on appetite provides insight into how these drugs are subtly reshaping our food preferences and redefining what we consider pleasurable to eat.
The Impact on Food Preferences and Cravings

As GLP-1 drugs modulate appetite, they also have a significant impact on food preferences and cravings. Users often report a decreased desire for sugary and fatty foods, which are typically associated with high pleasure but low nutritional value. This shift can lead to an increased appreciation for more nutritious options, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. The alteration in taste preferences not only supports healthier eating habits but also challenges the food industry to adapt. Manufacturers may need to innovate new products that cater to these changing tastes, potentially leading to a broader availability of healthier food options on the market.
Social and Cultural Implications of Altered Food Pleasure

The changing landscape of food pleasure due to GLP-1 drugs extends beyond individual experiences to influence social and cultural dynamics. Traditionally, food has been a central element of social gatherings and cultural rituals, often centered around indulgence and shared enjoyment of rich, flavorful dishes. As GLP-1 users experience a shift in their taste preferences, social norms around eating may evolve. This could lead to a reevaluation of culinary traditions, with a growing emphasis on health-conscious choices that still maintain the essence of communal dining. The cultural narrative around food pleasure is thus being rewritten, potentially fostering a more inclusive dialogue about health and enjoyment.
The Role of the Food Industry: Innovation and Adaptation

The food industry is at a crossroads, prompted by the evolving tastes of consumers influenced by GLP-1 drugs. As demand for healthier food options increases, companies are challenged to innovate and adapt. This could mean developing new recipes that cater to altered taste buds, reducing sugar and fat content while enhancing natural flavors. Additionally, there may be a push towards transparency in labeling and sourcing, as consumers become more conscious of their dietary choices. The industry’s response to these changes will be crucial in shaping the future of food production and consumption, balancing the need for health with the desire for taste.
Psychological and Emotional Dimensions of Eating
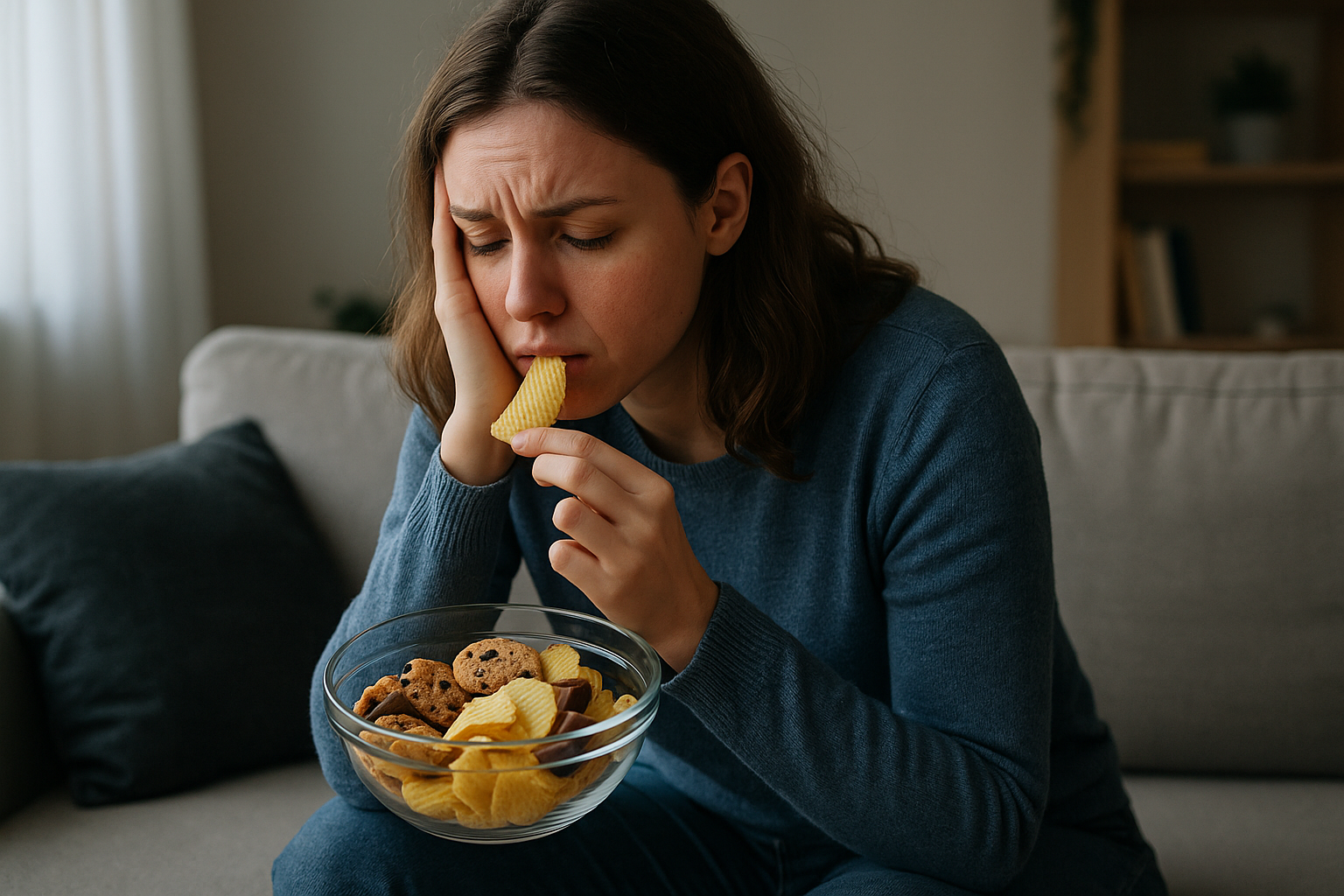

Beyond the physiological effects, GLP-1 drugs also impact the psychological and emotional aspects of eating. Food is often tied to emotions, serving as a source of comfort or a means of celebration. As these drugs alter the pleasure derived from certain foods, individuals may experience a shift in how they emotionally relate to eating. This can lead to a healthier relationship with food, where emotional eating is replaced by more mindful consumption. However, it also requires individuals to find new ways to fulfill emotional needs traditionally met by food, potentially encouraging the development of alternative coping mechanisms and sources of joy.
Future Prospects: A New Paradigm in Gastronomy
As we look to the future, the influence of GLP-1 drugs on food pleasure suggests a new paradigm in gastronomy. Chefs and culinary experts may explore innovative approaches to create dishes that align with the evolving tastes of consumers, emphasizing quality ingredients and balanced flavors. This could lead to a renaissance in the culinary arts, where the focus shifts from indulgence to nourishment without sacrificing taste. As GLP-1 drugs continue to gain popularity, they hold the potential to inspire a more health-conscious society, where food is celebrated not just for its taste but also for its role in promoting well-being. This transformation heralds a promising future for both individuals and the global food landscape.